Electric Vehicles are an Eco-Friendly Choice… Especially in Québec!
Electric vehicles are even more eco-friendly in Québec, where 99% of electricity comes from a clean, renewable source: the power of water.
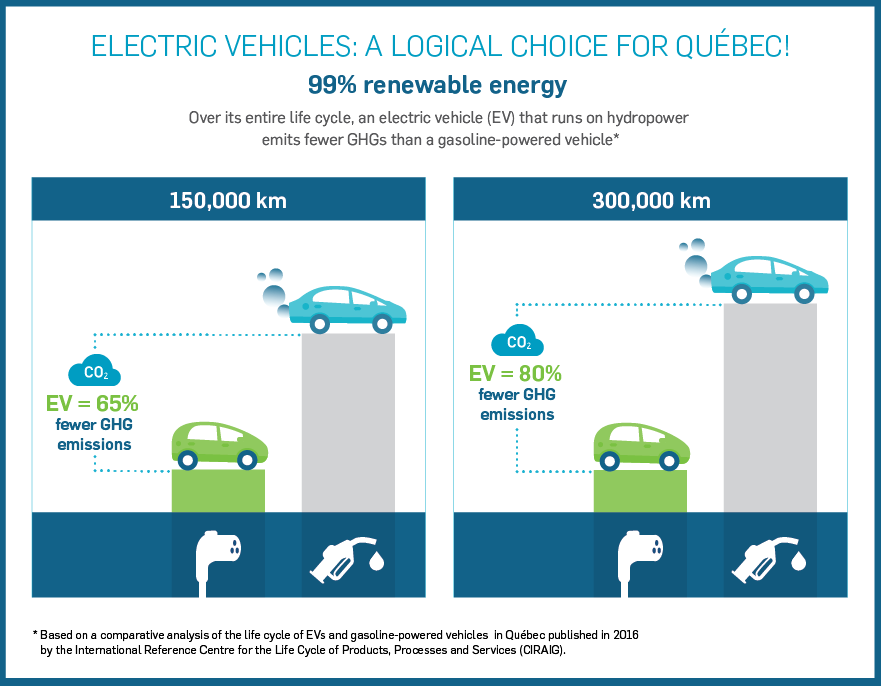
An electric vehicle is better for the environment over its entire life cycle than a gas-powered vehicle.
Electric vehicles produce much lower greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions than gas-powered vehicles. This is true even when taking into account the vehicle’s entire life cycle, from extracting the resources used to make it to scrapping it at the end of its life.
With an electric vehicle, the biggest environmental impact is produced during manufacturing. With an internal combustion vehicle, the greatest impact is generated during the utilization stage.
Polluting emissions by vehicle type
Gas-powered vehicles emit the most polluting emissions, followed by conventional hybrid vehicles. Plug-in hybrids emit still less polluting emissions than conventional vehicles. Electric vehicles produce no polluting emissions.
Source of energy
Consumption
Emissions
Conventional


Hybrid

Plug-in hybrid


All-electric
NO
EMISSIONS
