Glossary
Hydro‑Québec's Electricity Rate Terms
The Charter of the French language and its regulations govern the consultation of English‑language content .
Hydro‑Québec's Electricity Rate Terms
Amount of electricity that Hydro‑Québec supplies to a customer, expressed in kilovoltamperes (kVA). When it is used, apparent power breaks down into real power (kW), which runs devices, and reactive power (kVAR), which produces magnetic fields and which is not useful power for the customer.
The amount of power, expressed in kilowatts (kW), which the customer may not exceed for a given contract without the authorization of Hydro‑Québec.
Method of measuring energy consumed with a single meter instead of separate meters for an entire multiunit commercial or residential building. The building owner is responsible for dividing the costs between the occupants.
Period during which electricity is delivered to the customer and which extends between the two dates used by Hydro‑Québec for calculation of the bill.
Minimum demand that a large‑power industrial rate customer (Rate L) agrees to pay and that Hydro‑Québec must be ready to supply at any time in response to the customer’s demand.
Current, expressed in amperes (A), is the number of electrons carried by a conductor in one second. It is a function of voltage, expressed in volts (V), and resistance, expressed in ohms (Ω).
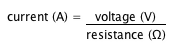
Power used by electrical equipment over a given period of time. Expressed in kilowatthours (kWh), energy is calculated as power, expressed in kilowatts (kW), multiplied by the time during which the power is used, expressed in hours (h).

A set amount, expressed in dollars per month or cents per day depending on the rate, to be paid for the electricity service itself.
Voltage of 44 kV or more.
A producer of electrical power who either consumes for its own needs or sells all or part of the electricity power it produces to a third party or to Hydro‑Québec.
Relationship between the energy (in kilowatthours) actually consumed and the amount of energy that can be consumed by using the entire maximum power demand throughout the consumption period. The load factor indicates the utilization rate of maximum power demand for a given consumption period.
Voltage of 750 V or less.
Maximum power measured during a consumption period. It is the higher of the following two values: real power in kilowatts (kW), or a percentage (90% for domestic rates and small- and medium‑power rates, or 95% for large‑power rates) of the apparent power in kilovoltamperes (kVA).
Voltage of more than 750 V, but less than 44 kV.
The minimum amount of power that the customer must pay for each consumption period, regardless of electricity use. The threshold is set so that you pay your share of the costs Hydro‑Québec incurs to meet your power needs at all times. The minimum billing demand is determined by the conditions of each rate, as indicated in the Electricity Rates.
Minimum amount billable for electricity service even if little or no electricity has been used in the billing period.
Period of 30 days, which may begin on any day of the month, established by Hydro‑Québec for billing purposes.
A factor that is applied to the fixed charge, to the consumption at the various energy price tiers and to the base billing demand, as applicable depending on the rate.
Total amount of electricity supplied at a given time. Expressed in kilowatts (kW), power is the combined effect of voltage, expressed in kilovolts (kV), and current, expressed in amperes (A).
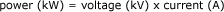
Ratio of real power (in kW) and apparent power (in kVA). The power factor is expressed as a percentage and indicates the efficiency with which the customer uses the electricity provided. Hydro‑Québec encourages its customers to maintain a power factor of at least 90% or 95%, depending on their rate.
Amount of electricity consumed in a useful manner to operate equipment, such as a motor or a heating or lighting system. Real power is expressed in kilowatts (kW).
Method of measuring energy consumed with a separate meter for each residential or commercial unit in a building.
Period from April 1 through November 30, inclusive.
Difference in electrical level between two points, expressed in volts (V).
Period from December 1 through March 31 of the next year, inclusive.
Period during which electricity is delivered to the customer and which extends between the two dates used by Hydro‑Québec for calculation of the bill.
Maximum power measured during a consumption period. It is the higher of the following two values: real power in kilowatts (kW), or a percentage (90% for domestic rates and small- and medium-power rates, or 95% for large-power rates) of the apparent power in kilovoltamperes (kVA).
Minimum demand that a large-power industrial rate customer (Rate L) agrees to pay and that Hydro‑Québec must be ready to supply at any time in response to the customer’s demand.
Amount of electricity consumed in a useful manner to operate equipment, such as a motor or a heating or lighting system. Real power is expressed in kilowatts (kW).
Total amount of electricity supplied at a given time. Expressed in kilowatts (kW), power is the combined effect of voltage, expressed in kilovolts (kV), and current, expressed in amperes (A).
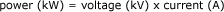
Difference in electrical level between two points, expressed in volts (V).
Power used by electrical equipment over a given period of time. Expressed in kilowatthours (kWh), energy is calculated as power, expressed in kilowatts (kW), multiplied by the time during which the power is used, expressed in hours (h).
The formula for energy is as follows: energy (in kilowatthours) is equal to power (in kilowatts) multiplied by duration of use (in hours).
Energy (kWh) = power (kW) x time used (h).
Amount of electricity that Hydro-Québec supplies to a customer, expressed in kilovoltamperes (kVA). When it is used, apparent power breaks down into real power (kW), which runs devices, and reactive power (kVAR), which produces magnetic fields and which is not useful power for the customer.