ENERGY STAR® certified TVs
Energy savings top the list
There’s plenty of choice in the television department. There are models for every taste: simple or sophisticated, small for the bedroom or giant for the living room. But the most important thing to consider is power use, of course. Always opt for an ENERGY STAR certified model!

ENERGY STAR® savings
The ENERGY STAR label can be found on standard size models all the way to large screen TVs with the latest features like 3D and Internet connectivity. They are typically 25% more energy-efficient than regular models and, in both active and standby mode, they save you money. Some old TVs may use more than 10 W on standby to run clocks, maintain channel memory or store recording instructions, but an ENERGY STAR certified model, recent or not, uses no more than 1 W.
Technical points
Types of screens
There are now four main types of screens to choose from.
- LCD—Liquid crystal display with fluorescent (CCFL) backlighting
- They draw very little power.
- LED—Liquid crystal display with LED backlighting
- Because LEDs are brighter, these models use 20% to 30% less energy than LCD televisions.
- Plasma—Cells containing electrically charged gases sandwiched between two sheets of glass
- They use more power than LCD TVs.
- Most of the big manufacturers have stopped making them.
- OLEDs (organic light-emitting diodes)—Every diode consists of layers of organic semiconductors containing oxygen, carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen atoms, and produces light that can be used in televisions. These are the most energy-efficient screens. They save 60% to 80% more than other screens, but they are fairly expensive.
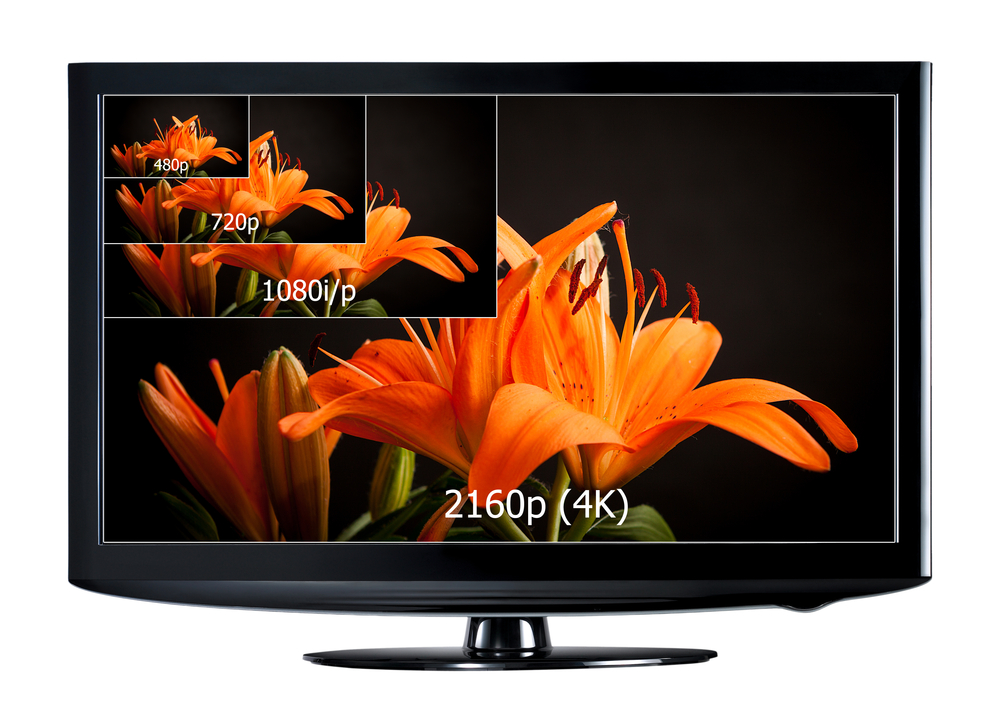
Screen definition
- HD—720p and full HD
- There are 720p and 1080p (progressive scan) screens and 1080i (interlaced) screens. Full HD refers to 1080p and 1080i screens. Interlaced scanning displays even rows first, then odd, while progressive scanning displays even and odd rows at the same time, which is why the picture is better and the TVs cost more.
- A screen with 1,080 rows has a resolution of 1,920 pixels x 1,080 and a screen with 720 rows has a resolution of 1,280 pixels x 720. That means that a picture displayed in 1,080i (more than 2,073,600 pixels) is more than twice as precise as one with 720p (921,600 pixels).
- Old CRT screen TVs have a resolution of only 480p, or 640 columns x 480 rows.
- Ultra-HD (UHDTV), or 4K
- The latest-generation 4K ultra-HD TVs have a minimum of 3,840 columns x 2,160 horizontal rows, or four times as many pixels as full HD.

TV size
Generally speaking, the bigger the screen, the more electricity the TV uses. So a TV with a 105-cmeters (52-in.) screen uses about 33% more energy than one with an 80-cmeters (42-in.) screen. Use the tables below to help you find the right screen for you.
What screen size is best for you?
Optimal viewing distance by the size of the television and the resolution
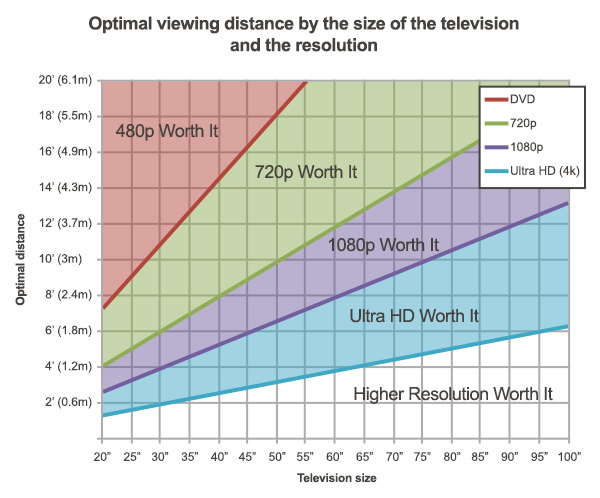
| Screen size | Optimal distance 1080p |
|---|---|
| 25 inches | 1 meter (39 in.) |
| 30 inches | 1.22 meters (48 in.) |
| 35 inches | 1.40 meters (55 in.) |
| 40 inches | 1.62 meters (64 in.) |
| 45 inches | 1.83 meters (72 in.) |
| 50 inches | 2.01 meters (79 in.) |
| 55 inches | 2.23 meters (88 in.) |
| 60 inches | 2.44 meters (96 in.) |
| 65 inches | 2.62 meters (103 in.) |
| 70 inches | 2.83 meters (111 in.) |
Display settings
Many TVs have default or predefined sports or movie settings. If you change the picture brightness and contrast, it affects the TV’s power use.
As manufacturers generally give priority to brightness, televisions use 25% more energy when one of those settings is selected instead of automatic brightness control. Most models have this mode. Be sure to use it to dim the brightness and, at the same time, use less power.