Understanding your bill with billing demand
Every bill is different. That’s because the amount to pay depends on your electrical installation’s power demand (greater than or equal to 50 kW) and how much electricity you’ve used.
The Charter of the French language and its regulations govern the consultation of English‑language content .
Every bill is different. That’s because the amount to pay depends on your electrical installation’s power demand (greater than or equal to 50 kW) and how much electricity you’ve used.
Transactions since your last bill: account balance prior to current bill, payments made, credits and amount due.
Message of general interest or information about our services.
Electricity costs, taxes, charges (if any) and amount of bill.
Total amount due and due date.
Return the stub with your payment if you pay by mail.

Transactions since your last bill: account balance prior to current bill, payments made, credits and amount due.
Message of general interest or information about our services.
Electricity costs, taxes, charges (if any) and amount of bill.
Total amount due and due date.
Return the stub with your payment if you pay by mail.
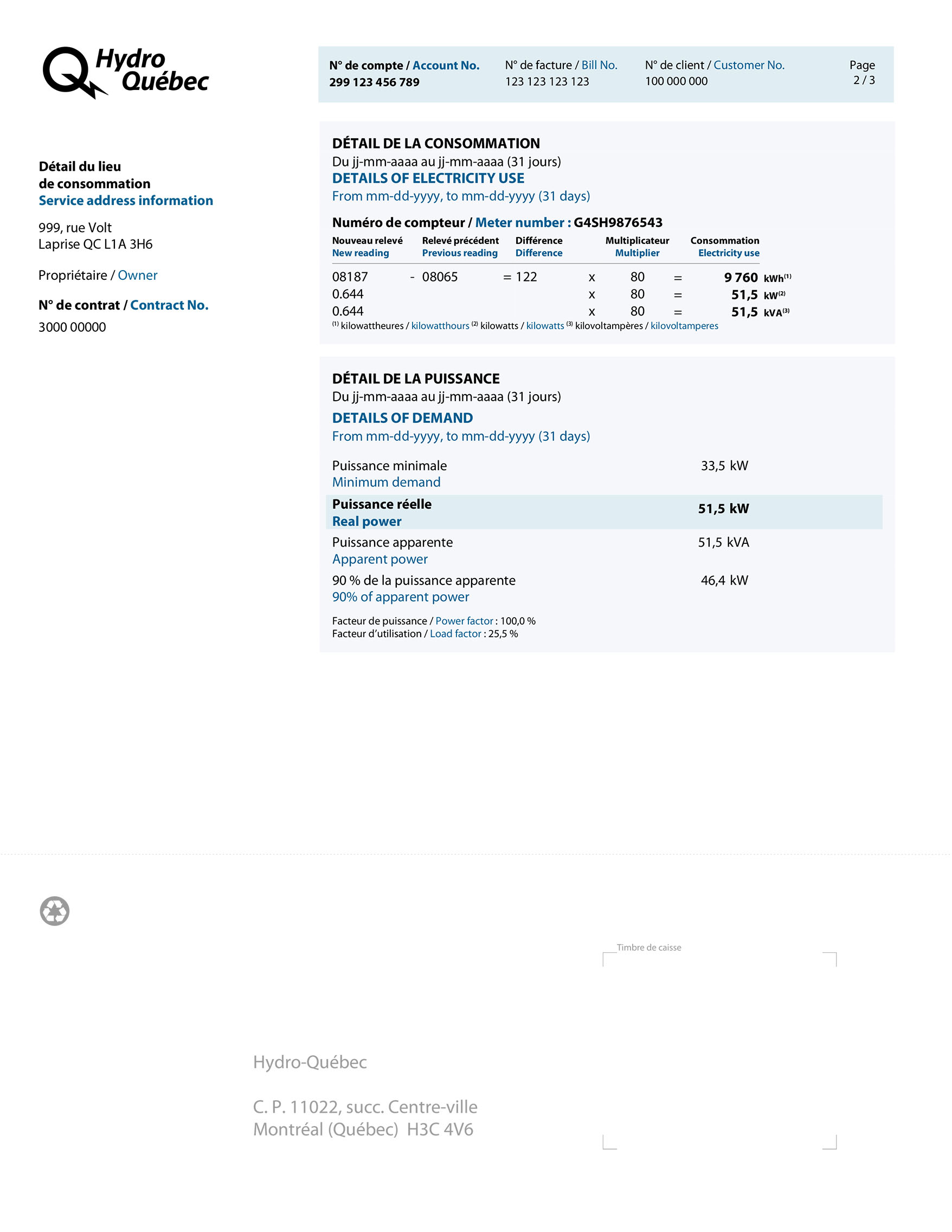
Service address, contract holder and contract number.
Period covered by bill, number of days, meter serial number, new and preceding meter readings and the amount by which they are multiplied to calculate your energy consumption (kWh) in the period.
New meter reading (08187) − previous reading (08065) = kilowatthours used (122) × multiplier (80) = kilowatthours used (9 760)
Note: To calculate power demand in kilovolt-amperes (kVA) and kilowatts (kW), you don’t need to calculate the difference between the current and previous reading, since power demand is reset after each reading.
Billing demand may be based on real power or apparent power. Real power, expressed in kW, is the electricity used to operate equipment such as lights, a heating system or a motor. Apparent power, expressed in kVA, is the maximum quantity of electricity that Hydro‑Québec must supply to its customers to ensure proper functioning of their equipment.
Minimum billing demand, i.e., 65% of the highest demand during a consumption period falling entirely within the winter period.
The largest real power demand during the consumption period.
The highest apparent power demand during the consumption period.
90% of the largest apparent power demand (90% x 51,5 = 46,4 kW)
The power factor is the ratio of real power demand to apparent power (51,5 ÷ 51,5 = 100,0 %).
The load factor is the ratio of actual energy consumption in kWh to the maximum power demand multiplied by the number of hours in the consumption period. In other words, it’s the ratio of the energy consumption over a given period to the number of kilowatthours that would have been consumed if maximum power had been drawn over all hours in the period (9 760 kWh ÷ (51,5 kW x 744 hours) = 25,5 %).
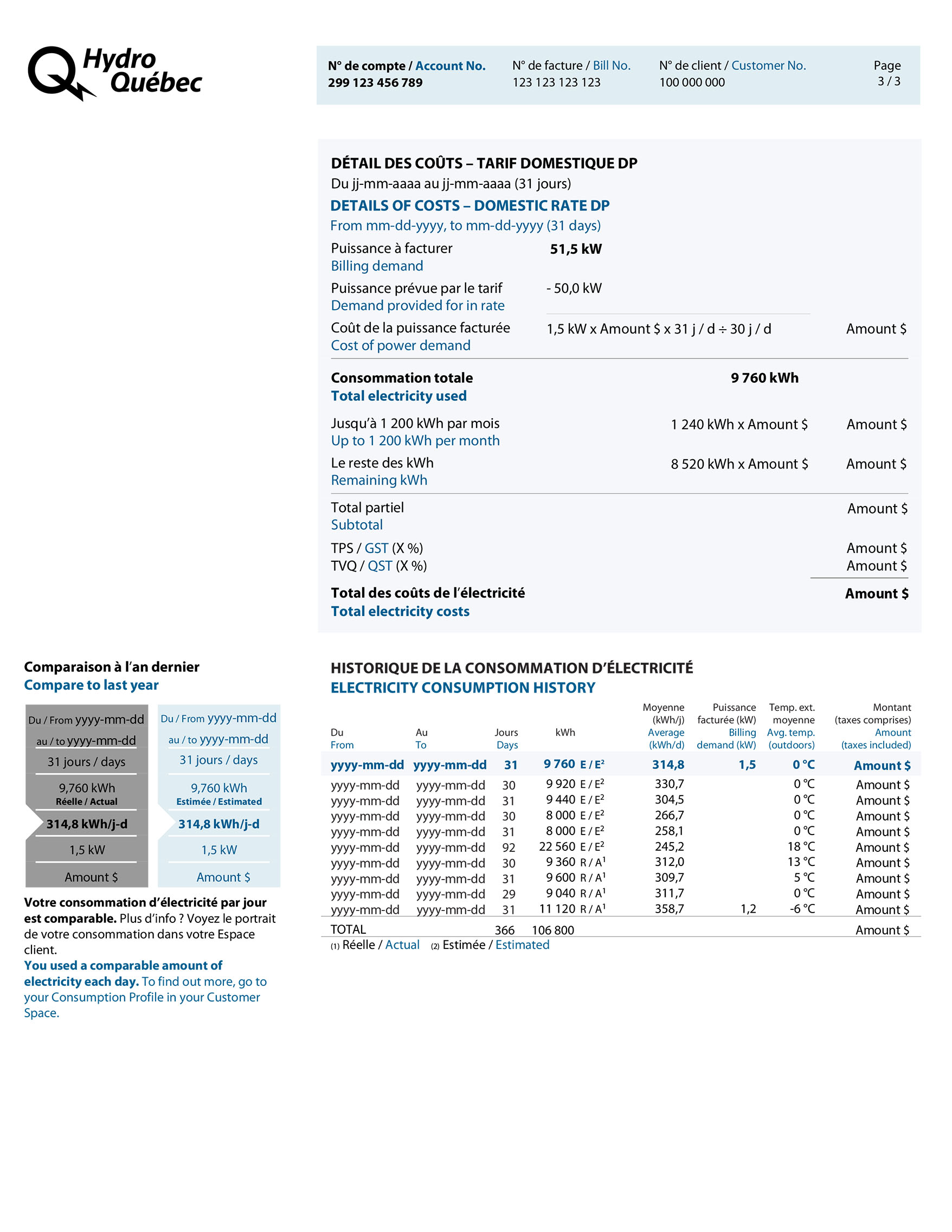
Detailed calculation of the cost of power demand and electricity used, based on applicable rates and number of days, credits or other charges (if applicable) plus taxes. The total is carried over to page 1, under the heading Summary of this bill.
Your billing demand is the higher of the following two values:
Billing demand = 51,5 kW (real power) > 46,4 kW (90% of apparent power) > 33,5 kW (minimum billing demand)
Demand is billed only if your power demand exceeds 50 kW.
The cost of power, based on billing demand in excess of 50 kW.
51,5 kW (billing demand) − 50,0 kW (demand provided for in rate) = 1,5 kW (cost of power demand)
Kilowatthours used in billing period = 9 760 kWh
Energy used, up to the product of 1 200 kWh per month in the billing period (1st tier). The total of 1 240 kWh is calculated as follows:
1 200 kWh × 31 days (days in billing period) ÷ 30 days (monthly period)
Electricity used beyond first tier (2nd tier). Here’s how it’s calculated:
9 760 kWh (kilowatthours used) − 1 240 (kilowatthours calculated in 1st tier) = 8 520 kWh
New table that compares a number of variables with the same period last year: number of days in period, total electricity use, average daily use, average outdoor temperature and electricity cost.
A personalized message tells you whether your average daily electricity use is higher, lower or similar to that of the same period last year.
You can see your electricity use in kilowatthours or in dollars and note how it changes from hour to hour using the Energy Performance Indicator in your Customer Space.
Information on your electricity use over the past year: period, number of days in the consumption period, total consumption, average daily consumption, billing demand and electricity cost.