Running-in of new equipment
by large‑power customers
Helping you carry out your projects
If you have to run short tests before putting new equipment or a new facility into service, your power demand may rise for a few months while you optimize operation.
Potential savings
By taking advantage of the conditions for running-in new equipment, you can get around this problem, simply by not having to pay for a momentary but significant increase in your power demand.
These conditions allow us to calculate your bill differently. More specifically, you are temporarily exempted from certain conditions that normally apply to power billing. This lets you test new equipment without having to pay for the resulting increase in your power demand during the running-in period.
Flexible terms and conditions
To take advantage of the running-in conditions, you must meet the following conditions:
- The power of the equipment being run in must equal at least 10% of the minimum billing demand in effect at the time you make your written request, but no less than 500 kW.
- You must advise Hydro‑Québec in writing at least 30 days before the start of the running-in period, specifying the consumption periods to which you want the running-in period to apply.
- You must send Hydro‑Québec a description of the type and power of your equipment for approval.
Calculation of billing amount during running-in period
Existing large‑power customers
An average price in cents per kilowatthour will be established based on the last 12 consumption periods during which there was no running-in, as well as Rate L or LG prices and conditions in effect during each consumption period to which running-in applied.
During the running-in period, the energy consumed is billed at this average price, plus to , depending on the relative size of the equipment being run in.
These conditions can apply from 1 to 12 consumption periods.
New large‑power customers
You must supply Hydro‑Québec with an estimate of the power demand and energy for the running-in period.
An average price in cents per kilowatthour will be established based on Rate L or LG prices and conditions in effect during each consumption period to which running-in applies.
During the running-in period, the energy consumed is billed at this average price plus .
Once three consumption periods have passed after the end of running-in, the bills issued for the running-in period will be adjusted according to the average price for these three periods, plus .
More information
If you have any questions about this rate, contact your commercial officer or designated agent. You can also reach our Business customer services by phone at 1 800 463‑9900 or by email at business@hydro.qc.ca.
This information has been simplified. For more details about the running-in option for large-power customers, consult Section 7 of Chapter 6 of the Electricity Rates [PDF 2.31 MB].
Power demand
Power a customer requires to meet energy needs at a given time. The higher the customer’s energy consumption at a given time, the higher the power demand.
Power
Total amount of electricity supplied at a given time. Expressed in kilowatts (kW), power is the combined effect of voltage, expressed in kilovolts (kV), and current, expressed in amperes (A).
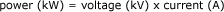
Minimum billing demand (minimum demand)
The minimum amount of power that customers must pay for each consumption period, regardless of their electricity use. The threshold is set so that customers pay their share of the costs Hydro-Québec incurs to meet their power needs at all times. The minimum billing demand is determined by the conditions of each rate, as indicated in the Electricity Rates.
- For all rates except Rate L, the minimum billing demand is automatically determined based on the previous winter’s maximum power demand.
- Rate L customers must set their own minimum billing demand, called “contract power,” based on their projected electricity use.
Consumption period
Period during which electricity is delivered to the customer and which extends between the two dates used by Hydro-Québec for calculation of the bill.
Energy
Power used by electrical equipment over a given period of time. Expressed in kilowatthours (kWh), energy is calculated as power, expressed in kilowatts (kW), multiplied by the time during which the power is used, expressed in hours (h).
The formula for energy is as follows: energy (in kilowatthours) is equal to power (in kilowatts) multiplied by duration of use (in hours).
