Rate LG
Structure of Rate LG
Billing for Rate LG includes the following:
- An amount for the energy in kilowatthours (kWh) consumed during the period in question.
- An amount for the billing demand in kilowatts (kW).
Rate LG is a monthly rate, which means the amount billed for power is based on a 30‑day period.
If applicable, the following may lower your bill:
The following may also be billed in certain cases:
Rate LG prices in effect
Breakdown of billing
Applicable in certain cases
- Credit for supply at medium or high voltage
- Voltage of 5 kilovolts (kV) to less than 15 kV $0.6869/kW
- Voltage of 15 kV to less than 50 kV $1.1008/kW
- Voltage of 50 kV to less than 80 kV $2.4576/kW
- Voltage of 80 kV to less than 170 kV $3.0063/kW
- Voltage of 170 kV or more $3.9726/kW
- Adjustment for transformation losses 19.930¢/kW
Rates in effect as of April 1, 2025. This table does not replace the Electricity Rates document in any way whatsoever.
More information
This information has been simplified. For more details about Rate LG, consult Section 2 of Chapter 5 of the Electricity Rates [PDF 2.31 MB].
How to request electricity service
Minimum billing demand (minimum demand)
The minimum amount of power that customers must pay for each consumption period, regardless of their electricity use. The threshold is set so that customers pay their share of the costs Hydro-Québec incurs to meet their power needs at all times. The minimum billing demand is determined by the conditions of each rate, as indicated in the Electricity Rates.
- For all rates except Rate L, the minimum billing demand is automatically determined based on the previous winter’s maximum power demand.
- Rate L customers must set their own minimum billing demand, called “contract power,” based on their projected electricity use.
Energy
Power used by electrical equipment over a given period of time. Expressed in kilowatthours (kWh), energy is calculated as power, expressed in kilowatts (kW), multiplied by the time during which the power is used, expressed in hours (h).
The formula for energy is as follows: energy (in kilowatthours) is equal to power (in kilowatts) multiplied by duration of use (in hours).

Power
Total amount of electricity supplied at a given time. Expressed in kilowatts (kW), power is the combined effect of voltage, expressed in kilovolts (kV), and current, expressed in amperes (A).
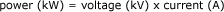
- Low voltage: Voltage of 750 volts (V) or less.
- Medium voltage: Voltage of more than 750 V, but less than 44 kilovolts (kV).
- High voltage: Voltage of 44 kV or more.
Voltage
Difference in electrical level between two points, expressed in volts (V).
Transformation
Operation that involves increasing or decreasing voltage through a transformer.
Power factor
Ratio of real power (in kW) and apparent power (in kVA). The power factor is expressed as a percentage and indicates the efficiency with which the customer uses the electricity provided. Hydro‑Québec encourages its customers to maintain a power factor of at least 90% or 95%, depending on their rate.
Maximum power demand
Maximum power measured during a consumption period. It is the higher of the following two values: real power in kilowatts (kW), or a percentage (90% for domestic rates and small- and medium-power rates, or 95% for large‑power rates) of the apparent power in kilovoltamperes (kVA).
Power demand
Power a customer requires to meet energy needs at a given time. The higher the customer’s energy consumption at a given time, the higher the power demand.
Winter period
Period from December 1 through March 31 of the next year, inclusive.
Rate
Electricity rate effective April 1, 2025.
